OOP Fundamental
Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) ภาษาไทย: การเขียนโปรแกรมเชิงวัตถุ เป็นรูปแบบการเขียนโปรแกรมชนิดหนึ่ง ที่นักพัฒนาให้การยอมรับ และเป็นที่นิยม (ในอดีต) สำหรับโปรแกรมที่เริ่มมีความซับซ้อน โดยมีลักษณะเบื้องต้น
- การมองโปรแกรมเสมือนวัตถุหนึ่งอย่าง เช่น นก รถยนต์
- การมองค่า หรือตัวแปรของโปรแกรม เป็นคุณสมบัติ เช่น นกมีน้ำหนัก 2 kg, รถยนต์ มีความเร็ว 60 km/hr
- การมองฟังก์ชันการทำงานของโปรแกรม เป็น พฤติกรรม เช่น นกบินได้, รถยนต์สามารถวิ่งไปข้างหน้าได้
OOP Backbone
- Encapsulation การห่อหุ้มข้อมูล
- Abstraction การรู้แค่ที่จำเป็น
- Inheritance การสืบทอดคุณสมบัติ
- Polymorphism การมีหลายรูปแบบ
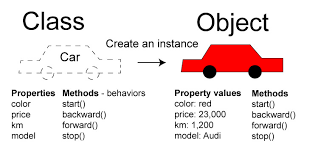
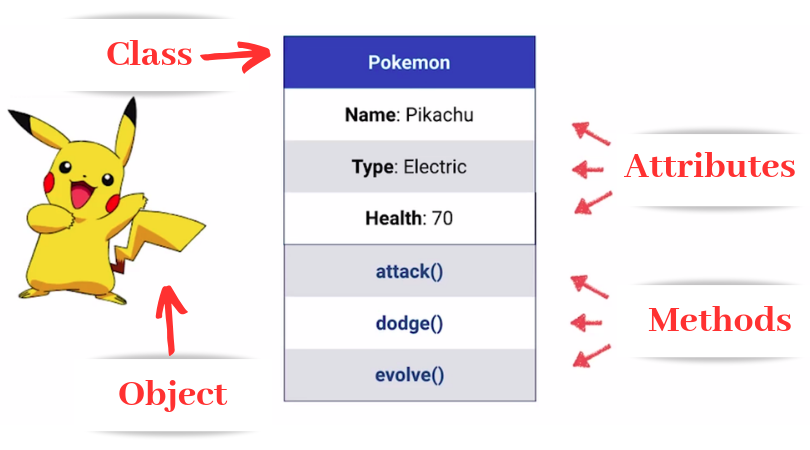
OOP Vocabulary
MethodคือFunctionของโปรแกรมนั้นๆ เปรียบเทียบกับพฤติกรรมหรือการทำงานของวัตถุAttributeคือVariableที่ระบุให้วัตถุนั้นๆ เปรียบได้กับ ตัวแปร หรือ ค่าคงที่ของโปรแกรมClassคือ การสร้างชนิดของข้อมูลใหม่ ตามที่เราต้องการ โดยอาศัยหลักการทำงานของ OOP เป็นพื้นฐาน สามารถระบุ method, attribute ได้ตามที่ programmer ต้องการObjectคือ ข้อมูลที่เกิดขึ้น หลังจากสร้าง class แล้ว เราสามารถสร้าง object ที่มี attribute ที่ต่างกันได้ โดยใช้พื้นฐานจาก class เดียวกันBlueprintหรือPrototypeคือสิ่งเดียวกับ class หลังจากสร้าง class แล้ว จะเปรียบเสมือนมีแม่แบบ ในการสร้าง Object ใดๆ ก็ได้ โดยใช้ method, attribute ของ class นั้นๆ
ใน JavaScript, class เป็นโครงสร้างที่ใช้สร้างวัตถุ (object) ที่มีคุณสมบัติ (properties) และพฤติกรรม (methods) คล้ายกับภาษาอื่นๆ เช่น Python หรือ Java แต่ภายใต้ระบบ prototype-based ของ JavaScript
Class Creation
Constructor
เป็นการกำหนด Attribute ให้กับ object ทำให้ object แต่ละตัวมีค่าที่แตกต่างกันได้
class Person {
constructor(name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
const john = new Person("John");
const mary = new Person("Mary")Method
เป็นการกำหนดการทำงาน (พฤติกรรม) ของ class ที่เราสร้างขึ้นมา ใช้หลักการเดียวกับฟังก์ชัน
class Person {
constructor(name, age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
introduce() {
console.log(`Hi, I'm ${this.name}, I'm ${this.age} years old.`);
}
}
const john = new Person("John", 20);
john.introduce();Modify attribute
- แก้ไขผ่าน Attribute (ไม่ควรทำ)
class Person {
constructor(name, age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
introduce() {
console.log(`Hi, I'm ${this.name}, I'm ${age} years old.`);
}
}
const john = new Person("John", 20);
john.age = 20;- ควรใช้หลักการ Encupsulation โดยใช้ผ่าน Private Field
class BankAccount {
#balance;
constructor(initialBalance) {
this.#balance = initialBalance;
}
deposit(amount) {
this.#balance += amount;
}
getBalance() {
return this.#balance;
}
}
const account = new BankAccount(1000);
account.deposit(500);
console.log(account.getBalance());
// console.log(account.#balance); // SyntaxError: Private field '#balance' must be declaredStatic Methods และ Attributes
เป็นสมาชิกของคลาสที่ไม่สามารถเข้าถึงผ่าน instance ได้ แต่สามารถเรียกใช้ผ่านคลาสโดยตรง
class MathUtil {
static PI = 3.14;
static square(x) {
return x * x;
}
}
console.log(MathUtil.PI);
console.log(MathUtil.square(5));Type checking
สามารถใช้ instanceof เพื่อตรวจสอบว่า object เป็น instance ของคลาสใด
console.log(account instanceof BankAccount); // true
console.log(john instanceof Person); // trueInheritance
เป็นการสืบทอด class โดยเราจะมองว่าโปรแกรมเชิงวัตถุ สามารถมีคุณสมบัติคล้ายคลึงกัน แต่เปลี่ยนแปลงบางอย่างได้ โดยจะเรียก class หลักว่า parent และ class ที่สืบทอดว่า child
โดย syntax ที่ต้องระบุเพิ่มได้แก่
- class ที่เป็น child ต้องระบุ class parent ตอนประกาศ class
- ถ้าต้องการสืบทอด properties และ attribute จาก parent ต้องใช้
super()
class Student extends Person {
constructor(name, age, studentId) {
super(name, age);
this.studentId = studentId;
}
getStudentId() {
return this.studentId
}
}
const alice = new Student("Alice", 17, "S12345");
alice.introduce();
console.log(alice.getStudentId());
Replace parent methods
class Student extends Person {
constructor(name, age, studentId) {
super(name, age);
this.studentId = studentId;
}
introduce() {
console.log(`Hi, I'm ${this.name}, I'm ${this.age} years old. ID: ${this.studentId}`);
}
getStudentId() {
return this.studentId
}
}
const alice = new Student("Alice", 17, "S12345");
alice.introduce();
console.log(alice.getStudentId());Exercise
- สร้าง class ของรถยนต์ (car) โดยมี properties และ method ดังนี้
- properties: สี, ชนิดของรถ, ความเร็ว (km/hr)
- method:
- ขับ (drive): ให้แสดงผล driving
- method คำนวนเวลาที่ใช้ในการเดินทาง: ให้รับค่า parameter เป็นระยะทาง จากนั้น ให้นำความเร็วมาหาร และแสดงผลเป็นเวลาที่ใช้ในการเดินทาง
- โจทย์
- ให้แสดงผลสีของรถยนต์ Benz
- ให้แสดงผลระยะเวลาที่ใช้ขับรถ BMW ถ้ากำหนดความเร็ว = 200, สี = black, ชนิดของรถ = sedan
- สร้าง class ของ Person กำหนดให้มีเพศ, อายุ, ชื่อจริง, นามสกุล จากนั้นให้สร้าง child class ชื่อ Student โดยให้สืบทอดคุณสมบัติของ Person แต่มีค่าที่เพิ่มมา คือ เลขประจำตัวนักเรียน และ ชั้นเรียน
- แสดงผล ข้อมูลบัตรประจำตัวนักเรียนเมื่อ
Student("male", 15, "Pathompat", "Sungpankhao", "67001202961", "grade 6") - ทดสอบแสดงผลชั้นเรียนของ
Person("female", 23, "Malinee", "Kunthong")
- แสดงผล ข้อมูลบัตรประจำตัวนักเรียนเมื่อ
Assignment
- เปลี่ยนฟังก์ชันและตัวแปรที่เคยใช้ใน assignment เดิมเป็น attribute และ method โดยสร้าง class ชื่อ
CourseOnlineUser- กำหนด attribute คือ id, username, password, firstname, lastname, course
- กำหนด method
login(username, password)getEnrollList()checkEnrollStatus(userId, courseName)updateEnrollment(userId, courseName, duration)
- กำหนดให้ run code นี้แล้วได้ผลลัพธ์ดังนี้
const mungCourses = [
{
name: "Programming 101",
status: "STUDYING",
totalDuration: 180,
takenDuration: 65,
expiredAt: "2025-07-20 00:00:00"
}
]
const mung = new CourseOnlineUser(1, "mungggy", "Test#1234", "Pathompats", "Sungpankhao", mungCourses);
mung.login("mungggy", "123456");
// Failed: invalid username & password
mung.login("mungggy", "Test#1234");
// Login success
mung.getEnrollList();
// Show mungCourses that status = ENROLLED
mung.checkEnrollStatus("Biology 101");
// Enroll not found
mung.checkEnrollStatus("Programming 101");
// Enroll found: Programming 101, status: STUDYING, duration: 65/180
mung.updateEnrollment("Programming 101", 30);
// Updated enroll: Programming 101, duration: 95/180
Reference


![[Part 6] JS: OOP & Inheritance](https://images.unsplash.com/photo-1489824904134-891ab64532f1?crop=entropy&cs=tinysrgb&fit=max&fm=jpg&ixid=M3wxMTc3M3wwfDF8c2VhcmNofDQ0fHxvYmplY3R8ZW58MHx8fHwxNzQ4OTM2NjA4fDA&ixlib=rb-4.1.0&q=80&w=1920)




![[Part 5] Frontend: Scaling Vue.js EP2](https://images.unsplash.com/photo-1653387137517-fbc54d488ed8?crop=entropy&cs=tinysrgb&fit=max&fm=jpg&ixid=M3wxMTc3M3wwfDF8c2VhcmNofDF8fHZ1ZXxlbnwwfHx8fDE3NTE3MDk3Nzl8MA&ixlib=rb-4.1.0&q=80&w=1140)
![[Part 4] Frontend: Scaling Vue.js EP.1](https://images.unsplash.com/photo-1607799279861-4dd421887fb3?crop=entropy&cs=tinysrgb&fit=max&fm=jpg&ixid=M3wxMTc3M3wwfDF8c2VhcmNofDF8fHZ1ZS5qc3xlbnwwfHx8fDE3NTExMzMwNDJ8MA&ixlib=rb-4.1.0&q=80&w=1140)
![[Part 3] Frontend: Modern Framework + Vue.js 3](https://images.unsplash.com/photo-1585076641399-5c06d1b3365f?crop=entropy&cs=tinysrgb&fit=max&fm=jpg&ixid=M3wxMTc3M3wwfDF8c2VhcmNofDN8fGpxdWVyeXxlbnwwfHx8fDE3NTA5NDYzMDl8MA&ixlib=rb-4.1.0&q=80&w=1140)